Spinal compression fractures can cause debilitating pain and limited mobility, particularly in individuals with conditions like osteoporosis, cancer, or trauma. Two of the most effective treatments for such fractures are vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, both of which are minimally invasive procedures aimed at stabilizing the spine and alleviating pain.
This guide explores the differences, benefits, procedures, and recovery processes associated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.
Understanding Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
What Is Vertebroplasty?
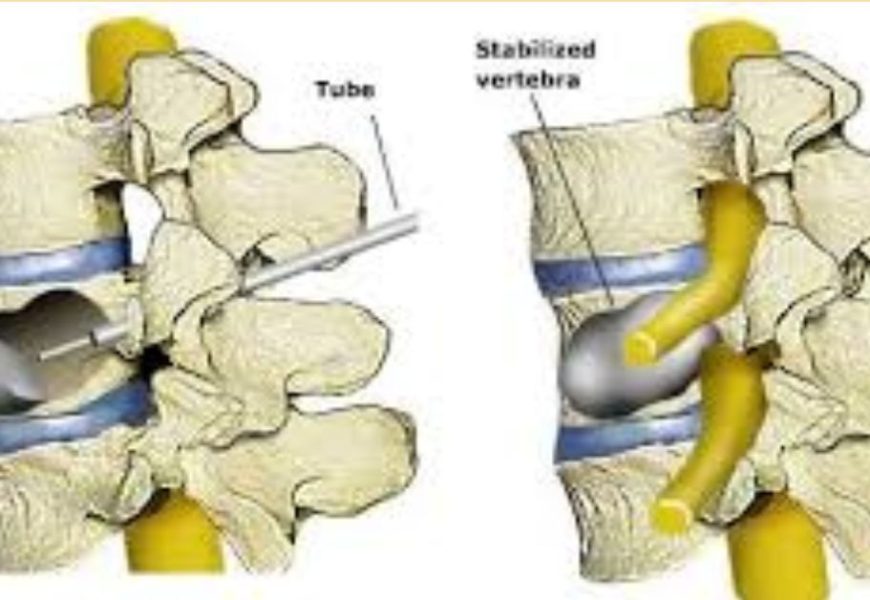
is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which bone cement is injected directly into a fractured vertebra. This stabilizes the bone, alleviating pain and preventing further collapse.
What Is Kyphoplasty?
Kyphoplasty is similar to vertebroplasty but includes an additional step. A small balloon is inserted into the vertebra and inflated to restore its height before the cement is injected. This technique can correct deformities caused by the fracture.
Conditions Treated by Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
Both procedures are commonly used to treat:
- Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Spinal Tumors or Metastases
- Traumatic Spinal Fractures (in select cases)
- Painful Vertebral Deformities
Key Differences Between Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Restoring Height: Kyphoplasty uses a balloon to restore vertebral height and alignment, while vertebroplasty does not.
- Pain Relief: Both procedures provide significant pain relief, but kyphoplasty may offer better results for deformity correction.
- Cost: Kyphoplasty is typically more expensive than due to its added complexity.
How the Procedures Are Performed
Diagnostic Imaging:
Patients undergo imaging studies like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to pinpoint the affected vertebra and assess the severity of the fracture.
Anesthesia:
Both procedures are performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and preference.
Accessing the Vertebra:
- A small incision is made in the back.
- A hollow needle (trocar) is guided into the fractured vertebra using fluoroscopy for precision.
Treatment:
- In Vertebroplasty: Cement is directly injected into the vertebra.
- In Kyphoplasty: A balloon is inserted and inflated to create a cavity and restore vertebral height before injecting the cement.
Finalization:
The cement hardens quickly, stabilizing the vertebra. The incision is closed, and the patient is moved to recovery.
Benefits of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
1. Pain Relief
Both procedures significantly reduce pain caused by vertebral fractures.
2. Improved Mobility
Stabilizing the spine enables patients to resume normal activities with less discomfort.
3. Quick Recovery
These minimally invasive techniques require less recovery time compared to traditional surgeries.
4. Preventing Further Damage
By stabilizing the spine, these procedures reduce the risk of further vertebral collapse.
Potential Risks and Complications
Although vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are considered safe, there are potential risks, including:
- Cement Leakage: Rare but may lead to nerve irritation or compression.
- Infection: At the injection site or within the spine.
- Nerve Damage: Due to improper needle placement.
- Adjacent Fractures: Increased stress on neighboring vertebrae can lead to new fractures.
Who Is a Candidate for Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty?
These procedures are ideal for patients who:
- Experience persistent back pain due to vertebral compression fractures.
- Have not responded to conservative treatments like medication, bracing, or physical therapy.
- Are in good overall health to tolerate a minimally invasive procedure.
Who Should Avoid These Procedures?
- Patients with asymptomatic fractures.
- Those with spinal instability requiring extensive surgery.
- Individuals with active infections or severe osteoporosis.
Recovery After Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
Immediate Recovery
- Most patients experience pain relief within 24 hours.
- Some soreness at the incision site is normal and usually subsides within a few days.
Long-Term Recovery
- Patients are encouraged to resume light activities within a day or two.
- Full recovery may take a few weeks, depending on the patient’s overall health and the extent of the spinal fracture.
Post-Procedure Care
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities for several weeks.
- Engage in physical therapy to strengthen the back and improve mobility.
- Follow up with the doctor to monitor spinal health.
Alternatives to Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
If these procedures are not suitable, other treatment options may include:
- Conservative Management: Pain relief with medications, rest, and bracing.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises to improve spinal stability.
- Spinal Fusion Surgery: For severe spinal instability or deformity.
Choosing Between Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
The choice between these procedures depends on several factors, including:
- Severity of Fracture: Kyphoplasty is better for fractures causing significant height loss or deformity.
- Cost and Availability: Vertebroplasty is generally more accessible and cost-effective.
- Doctor’s Recommendation: The treating physician will consider the patient’s overall health, fracture type, and goals.
Conclusion
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are transformative treatments for individuals suffering from painful spinal fractures. By understanding the purpose, process, and benefits of each procedure, patients can make informed decisions about their spinal health.
If you’re struggling with back pain or suspect a vertebral fracture, consult a spine specialist to determine whether vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is right for you. Both procedures offer hope for improved mobility and a better quality of life.